搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“大气科学 MODIS”相关记录29条 . 查询时间(0.093 秒)
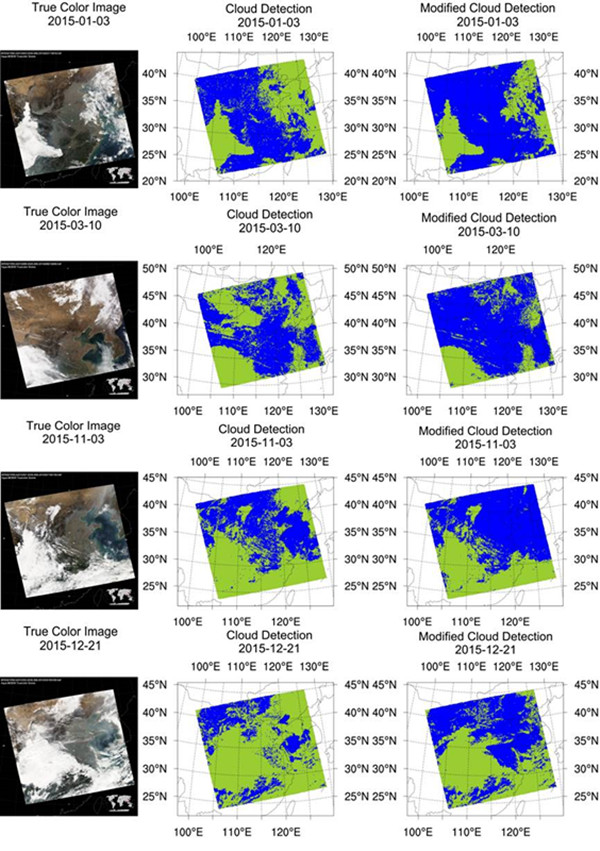
卫星遥感是获取云物理特征的主要途径之一。云特征的小量变化就可能显著影响地球的能量平衡。因此,云特征的准确观测非常重要。
MITIGATION ATMOSPHERIC EFFECTS IN INTERFEROGRAM WITH USING INTEGRATED MERIS/MODIS DATA AND A CASE STUDY OVER SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
MERIS MODIS Integration Interferogram correction
2018/5/15
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar(InSAR), as a space geodetictechnology, had been testified a high potential means of earth observation providing a method fordigital elevation model (DEM) and s...
基于MODIS EVI时序数据的江汉平原油菜种植分布信息提取
MODIS EVI 时间序列 油菜面积 江汉平原
2018/4/10
油菜是我国主要的食用油料作物。及时、准确地获取油菜种植分布信息对油菜长势监测、估产以及灾情评估具有十分重要的意义。以江汉平原为研究区,利用250 m空间分辨率的MODIS EVI时序数据,以TM数据作为野外采样数据与MODIS EVI数据之间的过渡数据,间接提取MODIS EVI数据农作物的训练样本; 通过分析江汉平原油菜和冬小麦的EVI光谱特征及物候信息,建立油菜种植面积提取模型; 采用多次阈值...
城市复杂地表TM温度反演及其与MODIS产品的比较
城市 复杂地表 温度反演 遥感
2013/9/26
在利用决策树模型将城市复杂地表分为植被、建筑物、水体、裸土等4类进行地表比辐射率估算和利用MODIS近红外数据反演大气水分含量的基础上,采用Jim nez-Mu oz单通道算法进行了城市复杂地表TM温度的反演,并将反演结果与EOSMODIS地表温度产品进行了比较分析。结果表明:(1)基于地表信息分类提取后的地表比辐射率和MODIS反演的大气水汽含量得到的地表温度接近于实际状况;(2)反演结果与EO...
渤海属中国内海,由于大量河流淡水注入,海水盐度仅为30PSU。渤海地处中纬度季风气候带,每年冬季都有不同程度的结冰现象,是北半球纬度最低的结冰海区。2009-2010年冬季,受北方持续寒潮的影响,渤海海域出现了持续低温天气,形成了近30年来最为严重的、罕见的、大范围的、持续的海冰灾情,给环渤海地区的港口、航运、渔业及海上作业等造成重大影响,快速准确地监测大范围海冰厚度分布及演化对于冰灾的防治具有重...
An analysis of the collection 5 MODIS over-ocean aerosol optical depth product for its implication in aerosol assimilation
the collection 5 MODIS over-ocean aerosol optical depth product aerosol assimilation
2011/1/20
As an update to our previous use of the collection 4 Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) over-ocean aerosol optical depth (AOD) data, we examined ten years of Terra and eight years o...
Global analysis of cloud field coverage and radiative properties, using morphological methods and MODIS observations
cloud field coverage radiative properties morphological methods MODIS observations
2011/1/19
The recently recognized continuous transition zone between detectable clouds and cloud-free atmosphere ("the twilight zone") is affected by undetectable clouds and humidified aerosol. In this study, w...
Cloud thermodynamic phase inferred from merged POLDER and MODIS data
Cloud thermodynamic phase merged POLDER and MODIS data
2010/12/28
The global spatial and diurnal distribution of cloud properties is a key issue for understanding the hydrological cycle, and critical for advancing efforts to improve numerical weather models and gene...
A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level 2 MISR aerosol products
the aerosol optical depth a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS Level 2 MISR aerosol products
2010/11/30
Using the ten-year (2000–2009) Data-Assimilation (DA) quality Terra MODIS and MISR aerosol products, as well as 7 years of Aqua MODIS, we studied both regional and global aerosol trends over oceans. T...
Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land
the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products land
2010/11/29
NASA's MODIS sensors have been observing the Earth from polar orbit, from Terra since early 2000 and from Aqua since mid 2002. We have applied a consistent retrieval and processing algorithm to both s...
Constraints on interactions between aerosols and clouds on a global scale from a combination of MODIS-CERES satellite data and climate simulations
aerosols clouds a global scale MODIS-CERES satellite data climate simulations
2010/10/21
Satellite-based cloud top effective radius retrieved by the CERES Science Team were combined with simulated aerosol concentrations from CCCma CanAM4 to examine relationships between aerosol and cloud ...
Biomass burning impact on PM 2.5 over the southeastern US during 2007: integrating chemically speciated FRM filter measurements, MODIS fire counts and PMF analysis
the southeastern US FRM filter measurements MODIS fire counts PMF analysis
2010/8/16
Archived Federal Reference Method (FRM) Teflon filters used by state regulatory agencies for measuring PM2.5 mass were acquired from 15 sites throughout the southeastern US and analyzed for water-solu...
A climatological perspective of deep convection penetrating the TTL during the Indian summer monsoon from the AVHRR and MODIS instruments
deep convection the TTL the Indian summer monsoon the AVHRR and MODIS instruments
2010/8/13
The impact of very deep convection on the water budget and thermal structure of the tropical tropopause layer is still not well quantified, not least because of limitations imposed by the available ob...
OMI and MODIS observations of the anomalous 2008–2009 Southern Hemisphere biomass burning seasons
OMI and MODIS the anomalous 2008–2009 Southern Hemisphere biomass burning seasons
2010/8/12
Significant inter-annual variability of biomass burning was observed in South America over the 2007–2009 period. The 2007 number of fires detected from space in South America, as well as the magnitude...
Saharan dust infrared optical depth and altitude retrieved from AIRS: a focus over North Atlantic–comparison to MODIS and CALIPSO
Saharan dust AIRS North Atlantic MODIS CALIPSO
2010/2/21
Monthly mean infrared (10 μm) dust layer aerosol optical depth (AOD) and mean altitude are simultaneously retrieved over the tropics (30° S–30° N) from almost seven years of Atmospheric Infrared Sound...

